수두증(뇌수종)과 선천성 뇌척수 기형, Hydrocephalus and congenital cerebrospinal abnormalities
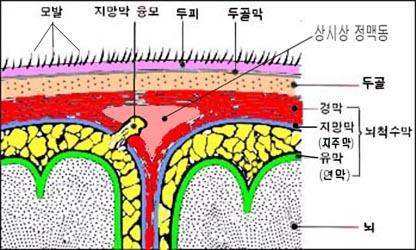
그림. 두피, 두개골 , 뇌막, 뇌
두통이 두피, 두개골 , 뇌막, 대뇌 등에 어떤 이상으로 생길 수 있다. 뇌막은 뇌를 싸고 있는 막으로서 경막, 지주막, 연막으로 구성된다. 경막을 경질막, 지주막을 거미막 또는 지망막, 연막을 유막 또는 연막질이라고 한다. 뇌와 척수를 둘러싼 막을 뇌척수막이라고 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
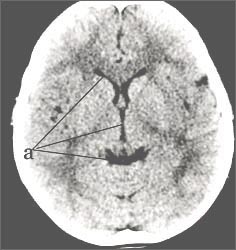
사진 1-80. 정상 뇌 CT 스캔 검사
정상 뇌실(a)
연세대학교 의과 대학 이규창 교수 제공
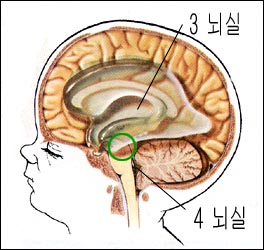
그림 1-83. 실비우스 뇌척수액 수도관이 막혀 생긴 수두증
출처: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus, Ohio,USA와 소아가정간호백과
뇌수막(뇌막), 뇌척수액의 분비, 흡수, 순환, 수두증
- 뇌막과 수막을 통틀어 뇌수막이 또는 뇌막이라고 한다.
- 중추신경계는 뇌와 척수(脊髓)로 구성되어 있다.
- 뇌와 척수는 뇌막과 수막으로 싸여 있다.
- 뇌척수막은 경막·지망막(지주막)·유막(연막)으로 구성되어 있다.
- 뇌수막을 뇌막 또는 뇌척수막이라고 한다(그림 000 참조).
- 지주막과 연막의 사이에 있는 공간에 뇌척수액(腦脊髓液)이 정상적으로 들어 있다.
- 뇌척수액은 뇌에 있는 융모막총(맥락총)에서 끊임없이 만들어지고 분비되는 것이 정상이다.
- 뇌척수액은 지주막과 연막 사이에 있는 지주막강·루시카좌 공·마젠디 공·외측 뇌실, 척수중심관 등을 통과하면서 끊임없이 순환된다.
- 뇌척수액은 뇌와 척수에 있는 지주막총을 통해서 혈관 속으로 정상적으로 흡수된다.
- 뇌척 수액이 생성되고 순환되고 흡수되는 과정 중 어떤 이상이 생기면 외측뇌실 속에 뇌척수액이 정상 이상으로 많이 괴어 외측뇌실이 비정상적으로 커지고, 두 개 강 내 압이 비정상적으로 증가되며 뇌 실질 양이 점점 작아지고 얇아지는 병을 수두증 또는 뇌수종이라고 한다.
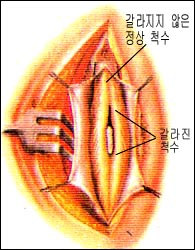
그림 1-90. 척수 정중익계
출처: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus Ohio,USA와 소아가정간호백과
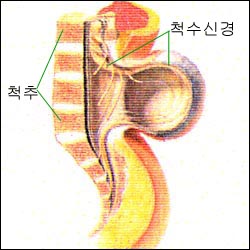
그림 1-88. 척수 수막류
출처: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus Ohio,USA와 소아가정간호백과
수두증(뇌수종)의 원인
- 수두증의 원인은 선천성 원인과 후천성 원인으로 나눈다.
- 자궁 내 병원체 감염으로 생긴 태아 감염병으로 수두증이 생길 수 있다.
- 뇌가 형성되는 과정에서 생긴 선천성 뇌 기형이나, 선천성 뇌 질환이 뇌척수액 순환 통로 일 부가 차단될 때 수두증이 생길 수 있다.
- 출생 후 뇌막염·뇌염·뇌 손상·뇌종양·비타민 A 과다증·비타민 D 과다증·약물 중독 등으로 수두증이 생길 수 있다.
수두증(뇌수종)의 분류
- 교통성 수두증,
- 비교통성 수두증,
- 뇌척수액 과도 분비성 수두증 세 가지로 분리하기도 한다.
수두증(뇌수종)의 증상 징후
- 수두증의 원인·중증도·종류 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 신생아들이나 첫 돌 전 영아들에게 수두증이 생기면 머리통이 비정상적으로 커질 수 있다.
- 수두증을 적절히 치료하지 않고 그대로 놓아두면 뇌척수액이 외측 뇌실 속에 점점 더 많이 괴고, 외측 뇌실 압이 비정상적으로 점점 더 증가되고 그로 인해 뇌 실질의 두께는 점점 더 얇아지고 두 개 강 내 전체 뇌척수액의 양이 비정상적으로 증가된다.
- 마지막으로 비정상적으로 증가된 두 개 강 내 압으로 두개골 두께도 점점 얇아지고 머리통 전체가 점점 더 커진다.
- 선천성 수두증을 가지고 태어난 신생아의 머리통은 비정상적으로 더 커져 있고, 출생 이후에도 점점 더 커질 수 있다.
- 두개골에 있는 여러 종류의 봉합(그림 1-1)이 비정상적으로 크게 벌어지고, 대천문과 소천문이 제때 막히지 않고 비정상적으로 커진다.
- 적절히 치료되지 않은 선천성 수두증이 있는 아이들의 성장발육이 지연되고 식욕부진· 구토 등 여러 가지 증상 징후가 생기고 비정상적으로 잠을 많이 잘 수 있고 경련 할 수 있다.
- 후천성으로 생긴 수두증의 증상 징후는 다양하다.
- 머리통이 비정상적으로 커지고, 구토, 시력장애, 정신 이상, 성격장애, 두통 등이 생길 수 있다.
- 소천문과 대천문은 생후 2세 전 정상적으로 막힌다.
- 대천문과 소천문이 막힌 이후 아이들에게 수두증이 생기면 두개골 봉합과 소천문과 대천문이 크게 벌어질 수 없어 머리통은 많이 커질 수 없다.
- 그 대신 두개강 내 압이 비정상적으로 증가되어 머리가 심하게 아프고 팔다리가 마비될 수 있으며 운동실조 등이 생길 수 있다. 뇌 종양,
수두증(뇌수종)의 진단
- 병력·증상 징후·진찰소견 등을 종합하여 수두증이 의심되면, 두개골 X-선 사진 검사·뇌 CT 스캔 검사·뇌 초음파 검사·뇌 MRI 검사·뇌척수액 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
수두증(뇌수종)의 치료
- 수두증의 원인·중증도·종류, 증상 징후 등에 따라 치료한다.
- 예를 들면, 뇌 종양으로 수두증이 생겼을 때는 뇌 종양과 수두증을 동시 치료한다.
- 약물 중독으로 생긴 수두증은 그 동안 치료에 썼던 약물을 더 이상 쓰지 않는다.
- 수두증의 원인을 근본적으로 제거해 치료할 수 없을 때는 수두증 완화 도관 측로(側路) 설치로 치료한다.
- 측 뇌실 속에 비정상적으로 많이 괸 뇌척수액을 두개강 내에서 두개강 밖으로 빼내는 도관 측로 설치수술로 수두증 완화치료를 할 수 있다.
- 도관측로 설치로 수두증을 치료할 때는 측뇌실 속과 우심방 속 사이를 연결하는 도관 측로, 측뇌실 속과 복막강 사이를 연결시키는 도관 측로, 또는 측뇌실 속과 척수 지주막 하 공간 사이를 연결하는 도관 측로 설치로 치로 할 수 있다.
- 측뇌실 속 뇌척수액이 도관 측로를 통과해서 복막강 속이나 우심방 속 또는 척수 지주막하 공간 속으로 흘러 들어가게 해서 수두증 완화 치료를 해 준다.
- 수두증을 도관 측로로 완화 치료해 주는 방법은 임시 수두증 치료방법이지 근본 수두증 치료방법이 아니다.
- 어떤 수두증을 약물로 치료해 줄 수 있다. 어떤 종류의 수두증은 자연적으로 치료되기도 한다.
|
다음은 “아이가 울면 구토를 해요 수두증(뇌수종/水頭症)과 선천성 뇌척수 기형”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 아이가 울면 구토를 해요 수두증(뇌수종/水頭症)과
선천성 뇌척수 기형
Q.
2001년 7월 24일생 남아입니다.
뇌막 뇌탈수증으로 인해 수술을 출생 한 달 후 하였습니다.
현재 수술경과 및 아이의 상태는 아주 양호합니다. 그런데 울음이 조금 길면 바로 구토를 합니다.
왜 그런지 알려주세요.
감사합니다.
A.
순님
- 안녕하세요. 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 좋은 질문입니다.
- 자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
- 여러 가지 이유로 구토를 할 수 있습니다.
- 누구든지 심하게 울 때 뇌압이 정상적으로 일시적으로 조금 더 올라갈 수 있습니다.
- 혹시 자녀가 우는 동안 뇌압이 비정상적으로 조금 더 올라가서 구토를 하는지 의심해 봅니다.
- 어떤 아이는 조금 흥분해도 구토합니다.
- 자녀의 경우 뇌막 뇌탈수증 수술치료를 받을 때 때로는 뇌실 복(막)강 션트 설치 치료를 할 수도 있습니다.
- 그 션트를 도관측로라고도 한다.
- 그런데 뇌실 복막강 션트 도관 측로가 막힐 때 뇌압이 올라가서 구토를 할 수 있습니다.
- 그 도관 측로에 밸브 장치가 있는데 그 밸브 장치의 기능이 제대로 되지 않을 수도 있습니다.
- 그 때 뇌압이 비정상적으로 더 증가되고 구토할 수 있습니다.
- 그 외 원인으로 구토할 수 있습니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 이 문제에 관해 상담하시기 바랍니다.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제 9권 소아청소년 소화계 질환–구토. 수두증(뇌수종 水頭症)과 선천성 뇌척수 기형 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원
Hydrocephalus and congenital cerebrospinal abnormalities
Fig. scalp, skull, meninges, brain
Headaches can be caused by any abnormality in the scalp, skull, meninges, or cerebrum. The meninges are the membranes surrounding the brain and are composed of the dura, arachnoid, and smoke membranes. The dura mater is called the dura mater, the arachnoid membrane, the arachnoid membrane or the arachnoid membrane, and the smoke membrane is called the oil membrane or the arachnoid membrane. The membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord is called the meninges. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Picture 1-80. Normal brain CT scan Normal ventricle
(a) Provided by Professor Kyu-Chang Lee, College of Medicine, Yonsei University
Figure 1-83. Sylvian cerebrospinal fluid hydrocephalus due to blockage of the aqueduct Source: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus, Ohio, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing written by John’s Lee, MD. FAAP
Meninges (meninges), cerebrospinal fluid secretion, absorption, circulation, hydrocephalus
• The meninges and meninges are collectively called the meninges or meninges.
• The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord.
• The brain and spinal cord are surrounded by meninges and meninges.
• The meninges are composed of the dura mater, the arachnoid membrane (arachnoid membrane), and the oil membrane (smoke membrane). • The meninges are called the meninges or meninges (see Figure.
• Cerebrospinal fluid (腦脊髓液) is normally contained in the space between the arachnoid and the soft film.
• It is normal for cerebrospinal fluid to be constantly produced and secreted by the chorionic plexus (choroid plexus) in the brain.
• Cerebrospinal fluid is constantly circulated as it passes through the arachnoid cavity, the Lucica seat ball, the Majendi ball, the lateral ventricle, and the central spinal canal between the arachnoid and the soft membrane.
• Cerebrospinal fluid is normally absorbed into blood vessels through the arachnoid plexus in the brain and spinal cord.
• If any abnormality occurs during the process of cerebrospinal fluid production, circulation, and absorption, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates abnormally in the lateral ventricle, causing the lateral ventricle to grow abnormally, the intracranial pressure to increase abnormally, and the amount of brain parenchyma to gradually decrease. The thinning disease is called hydrocephalus or hydrocephalus.
Figure 1-90. Spinal midline system Source: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus Ohio, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing
Figure 1-88. spinal meningitis Source: Used with permission from Ross Lab Columbus Ohio, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing
Causes of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus)
• Causes of hydrocephalus are divided into congenital and acquired causes.
• Hydrocephalus may be caused by an infectious disease of the fetus caused by an intrauterine pathogen infection.
• Hydrocephalus can occur when a part of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation pathway is blocked due to a congenital brain malformation or congenital brain disease that occurs during brain formation.
• After birth, meningitis, encephalitis, brain injury, brain tumor, vitamin A overdose, vitamin D overdose, and drug addiction can cause hydrocephalus.
Classification of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus)
1. traffic hydrocephalus,
2. Incomparable hydrocephalus,
3. Cerebrospinal fluid hypersecretory hydrocephalus is sometimes divided into three.
Signs of symptoms of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus)
• Symptoms and signs differ depending on the cause, severity, and type of hydrocephalus.
• Headaches can become abnormally large in newborns or pre-first-born infants with hydrocephalus.
• If hydrocephalus is left untreated, more and more cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the lateral ventricle, and the lateral ventricle pressure increases abnormally and gradually increases, resulting in a progressively thinner brain parenchyma and a decrease in the total amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. abnormally increased.
• Finally, due to the abnormally increased intracranial pressure, the skull becomes thinner and the entire head becomes larger. • Newborns born with congenital hydrocephalus have an abnormally large head, which may grow larger after birth.
• Various types of sutures in the skull (Fig. 1-1) are abnormally wide open, and the large and small portals are not blocked in time and are enlarged abnormally.
• Children with congenital hydrocephalus, which are not properly treated, may experience delayed growth and development, anorexia and vomiting, and may have abnormal sleepiness and convulsions. • Symptoms of acquired hydrocephalus are diverse.
• Headache becomes abnormally large, and vomiting, visual disturbances, mental disorders, personality disorders, and headaches may occur.
• Small and large astronomy are normally blocked before 2 years of age.
• If a child develops hydrocephalus after the large and small obelisks are blocked, the skull cannot be sutured and the small obliques and grand obliques cannot open wide, so the head cannot grow much. • Instead, the intracranial pressure increases abnormally, which can cause severe headaches, paralysis of limbs, and ataxia. brain tumor,
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus)
• If hydrocephalus is suspected by combining the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, it can be diagnosed with a cranial X-ray examination, brain CT scan, brain ultrasound examination, brain MRI examination, and cerebrospinal fluid examination.
Treatment of hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus)
• Treat according to the cause, severity, and type of hydrocephalus and symptoms and signs.
• For example, if hydrocephalus is caused by a brain tumor, treat the brain tumor and hydrocephalus simultaneously.
• Hydrocephalus caused by drug addiction no longer uses the drugs used to treat it.
• When the cause of hydrocephalus cannot be treated by radically removing it, treatment is performed by installing a hydrocephalus relief conduit.
• Hydrocephalus palliative treatment can be performed by installing a conduit to drain the abnormally large amount of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity to the outside of the cranial cavity in the lateral ventricle.
• When treating hydrocephalus by installing a conduit, a bypass connecting the inside of the lateral ventricle and the right atrium, a bypass connecting the inside of the lateral ventricle and the peritoneal cavity, or a bypass connecting the inside of the lateral ventricle and the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord can be done with teeth
• It relieves hydrocephalus by allowing the cerebrospinal fluid in the lateral ventricle to flow into the peritoneal cavity, the right atrium, or into the subarachnoid space through the lateral conduit. • The method of palliative treatment of hydrocephalus by catheterization is a temporary treatment for hydrocephalus, not a treatment for basic hydrocephalus. • Some hydrocephalus can be treated with medication. Some types of hydrocephalus can be cured spontaneously.
The following is an example of a Q&A on health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet regarding “Children vomit when they cry.
Q&A. When the child cries, he vomits. Hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus) and congenital cerebrospinal malformation
Q. He is a boy born on July 24, 2001. Surgery was performed one month after birth due to meningeal encephalopathy. Currently, the surgery and the child’s condition is very good. However, if you cry for a long time, you will immediately vomit. Please tell me why. thank you.
A. Sunnim • Hello. Thanks for asking. That’s a good question.
• The more information you have, such as your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical tests, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will give you an answer based on the information you provided.
• Vomiting can occur for a number of reasons. • When someone cries hard, the pressure in the brain may rise a little bit higher, normally temporarily.
• Suspect if your child vomits due to an unusually high level of intracranial pressure while crying.
• Some children vomit even with a little excitement.
• Your child may sometimes be treated with a ventricular peritoneal (membrane) shunt when undergoing surgical treatment for meningeal encephalopathy.
• The shunt is also called a conduit. • However, when the ventricular peritoneal shunt catheter is blocked, intracranial pressure rises, which can lead to vomiting.
• There is a valve mechanism in the conduit bypass, but that valve mechanism may not function properly. • At that time, the intracranial pressure rises abnormally higher and you may vomit.
• You may vomit for other reasons. • Please visit the Department of Pediatrics for a diagnosis and discuss this issue.
www.drleepediatrics.com – Vol. 9 Children’s and adolescent digestive system diseases – Vomiting. See also hydrocephalus (hydrocephalus) and congenital cerebrospinal malformations. • If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact us. thank you. Lee Sang-won
출처와 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Neurology in Pediatrics, P. F. Bray, Yearbook Medical Publishers
-
Behavior Disorders in Children, Bakwin and Bakwin
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 의학 용어사전 대한 의사 협회
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.