신경계의 구조, Anatomy of the nervous system
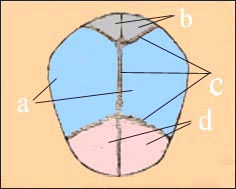
그림 1-1. 윗면 두개골과 두개골 봉합
a-두정골, b-후두개골 , c-봉합, d-전두개골
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
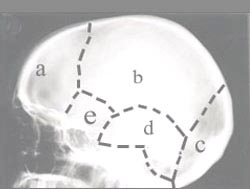
사진 1-2. 측면 두개골 X-선 사진
a-전두개골, b-두정골, c-후두개골 , d-측두개골 , e-접형골
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
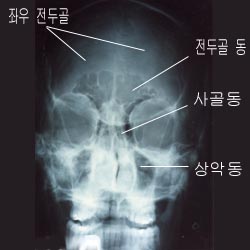
사진 1-3. 두부 전후 X-선 사진과 부비동.
a-좌우 전두개골 , b-좌우 전두동, c-상악 동
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
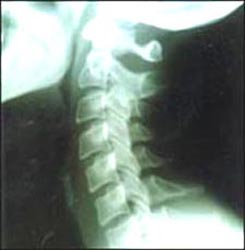
사진 1-4. 경부 척추(경추). 경부척추는 7개의 척추로 구성됐다
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
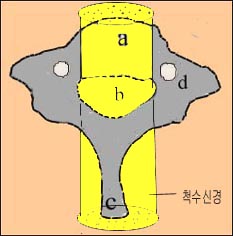
그림 1-8. 한 개의 척추
a-척추 체, b-척수가 들어있는 구멍,
c-척추 돌기(극돌기)
d-척추의 횡돌기 공
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
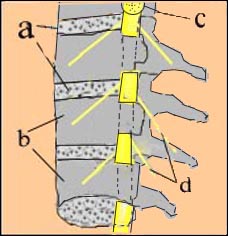
그림 1-9. 척주와 척수 신경
a-디스크, b-척추 체, c-척수 신경
d-말초 신경
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
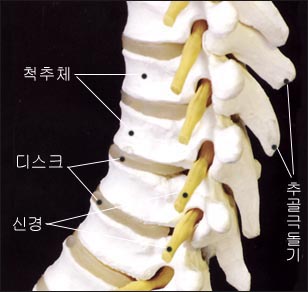
그림 1-10. 척추(척추뼈)
출처; American Academy of Pediatrics
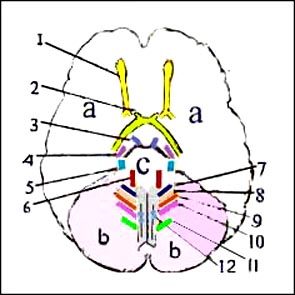
그림 1-12. 뇌저 전후면과 12 쌍 뇌신경 기시부
a-대뇌,
b-소뇌,
c-뇌교(교뇌),
d-연수,
1-후각 신경(I),
2-시신경 및 망막(II), 3-동안 신경(III),
4-활차 신경(IV),
5-외전 신경(V),
6-3차 신경(VI),
7-안면 신경(VII),
8-전정달팽이신경(VIII), 9-설인 신경(IX),
10-미주 신경(X),
11-척수 부신경(XI), 12-설하 신경(XII)을 통틀어
12쌍 뇌신경이라 한다
참조문헌; Gray’s Anatomy
|
☞ 신경 자극에서 반응까지. 자극 → 감각기 → 감각신경 → 반사중추(연수, 척수)→ 운동신경 → 운동기 → 반응 |
Anatomy of the nervous system

Figure 1-1. Upper skull and cranial sutures a-parietal bone, b-occipital skull, c-suture, d-frontal skull Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 1-2. Lateral skull x-ray a-frontal skull, b-parietal bone, c-occipital skull, d-temporal skull, e-sphenoid bone Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 1-3. X-ray before and after head and sinuses. a-left and right frontal sinuses, b-left and right frontal sinuses, c-maxillary sinuses Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 1-4. cervical vertebrae (cervical vertebrae). The cervical vertebrae are made up of 7 vertebrae. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-8. one spine a – vertebral body, b – cavity containing the spinal cord, c-vertebral process (spinal process) d – the ball of the transverse process of the spine Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-9. spinal column and spinal nerves a – disc, b – vertebral body, c – spinal nerve d – peripheral nerve Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 1-10. spine (vertebrae) source; American Academy of Pediatrics

Figure 1-12. The anterior and posterior floor of the brain and the origin of 12 pairs of cranial nerves
a – cerebrum,
b – cerebellum,
c – pons,
d -The 12 Cranial Nerves
☞ From nerve stimulation to response. Stimulation → sensory → nerve → reflex center (medulla oblongata, spinal cord) → motor nerve → motor → reaction
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.