윌슨 병, Wilson disease
윌슨 병의 개요
-
구리가 신진대사 이상으로 뇌, 간, 신장, 눈 등 신체의 각 계통의 여러 기관에 정상 이상으로 많이 축적되어 그 기관이 퇴화되고 그로 인해서 정신 이상, 간염, 혈뇨, 용혈성 빈혈 등을 동반하는 유전성 질환을 윌슨병이라고 한다.
-
([부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제14권 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병 질환 참조)
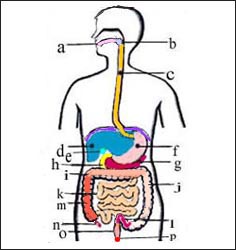
그림 2. 소화기계(소화계) 해부도
a-입, b-인두, c-식도, d-간, e-담낭, f-위, g-췌장, h-십이지장, i-횡행결장, j-하행결장, k-소장, l-S상결장, m-상행결장, n-충수, o-직장, p-항문
윌슨 병이 있으면 간과 뇌에 뚜렷한 병변이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
윌슨 병의 원인
-
이 병은 상염색체 열성으로 유전된다.
-
구리가 담즙을 통해서 정상적으로 분비되지 않아서 간세포 내에 구리가 비정상적으로 축적된다. 거기다가 전신 각 계통의 기관과 조직에도 비정상적으로 구리가 축적된다.
-
이 병은 생후 5세 이전 영유아들에게도 생길 수 있지만 5세 이후 유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들에게 주로 생긴다.
-
10~50만 명의 신생아들 중 한 명이 이 병에 걸릴 수 있다.
-
돌연변이로 비 전형적인 윌슨 병이 5세 이전 영유아들에게 생겨 그로 인해 간염이 생길 수 있다.
윌슨 병의 증상 징후
-
행동 이상, 손 떨림, 음식물 삼키는데 이상, 침을 많이 흘림, 당뇨, 뼈 이상, 급성 간염 또는 만성 간염, 간 비대증, 간부전증, 복수, 부종, 식도 출혈, 성장 지연증, 월경 불순증, 근육 강직증, 학습 부진, 빈혈, 신장 부전증, 요산 뇨증, 관절염 등이 나타날 수 있다.
- Kayser–Fleischer ring 이 양누에 나타 날 수 있다.
윌슨 병의 진단
-
환아의 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견과 적절한 임상검사 등을 종합해서 진단한다.
-
특히 5세 이후 유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들에게 원인 불명의 급성 간염 또는 만성 간염이나 간 질환, 신경 정신이상, 행동 이상, 뼈 이상, 빈혈, 신장 이상 등이 있을 때 이 병을 일단 의심해 볼 수 있다.
-
윌슨병이 있으면 혈 중 세룰로플파스민(Serum Ceruloplasmin)의 농도가 정상 이하로 낮고 혈청 구리 농도가 비정상으로 증가 될 수 있다.
-
소변 구리 분비가 비정상으로 높으면 이 병을 진단하는데 많은 도움이 된다.
-
간 생체조직 현미경 검사를 하면 간 구리 농도가 비정상으로 높은 결과를 발견할 수 있다.
- Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and γ-glutamyltransferase 혈 농도 증가, 동 농도 감소, 뇌 MRI 변화로 진단한다. 소스: N Engl J Med 2012; 366:e18March 22, 2012
Wilson disease
Overview of Wilson’s disease
• Copper accumulates more than normal in various organs of the body, such as the brain, liver, kidney, and eyes, due to metabolic abnormalities, and the organs are degenerated. The disease is called Wilson’s disease.
www.drleepediatrics.com – Vol. 14 Pediatric Endocrinology, Genetics, Chromosomes, Metabolism, and Rare Diseases)

Figure 2. Digestive system (digestive system) anatomy a – mouth, b – pharynx, c – esophagus, d – liver, e – gallbladder, f – stomach, g – pancreas, h – duodenum, i – transverse colon, j – descending colon, k – small intestine, sigmoid colon, m – ascending colon, n – appendix, o – rectum, p – anus Wilson’s disease can cause marked lesions in the liver and brain. Copyright Ⓒ 2013 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
Causes of Wilson’s disease
• The disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait.
• Copper is not normally secreted through bile, so copper accumulates abnormally in hepatocytes. In addition, copper is abnormally accumulated in organs and tissues of each system of the body.
• The disease can also occur in infants before the age of 5 years but occurs mainly in infants after 5 years of age, school-age children, and adolescents.
• One in 100,000 to 500,000 newborns may develop the disease.
• Mutations can cause atypical Wilson’s disease in children before age 5, resulting in hepatitis.
Symptoms, signs of Wilson’s Disease
• Behavioral abnormalities, hand tremors, abnormal swallowing, drooling, diabetes, bone abnormalities, acute or chronic hepatitis, hepatomegaly, hepatic insufficiency, ascites, edema, esophageal bleeding, growth retardation, dysmenorrhea, ankylosing of muscles , learning difficulties, anemia, renal failure, uric aciduria, arthritis, etc. may appear.
• Kayser–Fleischer rings may appear in both silkworms.
Diagnosis of Wilson’s disease
• Diagnosis is made by synthesizing the child’s past medical history, family history, symptomatic signs, examination findings, and appropriate clinical tests.
• Especially in infants after 5 years of age, school-age children, and adolescent children, when they have acute or chronic hepatitis of unknown cause, liver disease, neuropsychiatric disorders, behavioral disorders, bone disorders, anemia, or kidney disorders, this disease should be suspected. can
• With Wilson’s disease, serum levels of Serum Ceruloplasmin may be subnormally low and serum copper levels may be abnormally elevated.
• Abnormally high urine copper secretion is very helpful in diagnosing this disease.
• Liver biopsy microscopy may reveal abnormally high levels of copper in the liver.
• Alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and γ-glutamyltransferase increase in blood concentration, decrease in sinus concentration, and changes in brain MRI. Source: N Engl J Med 2012; 366:e18March 22, 2012
출처와 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Neurology in Pediatrics, P. F. Bray, Yearbook Medical Publishers
-
Behavior Disorders in Children, Bakwin and Bakwin
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 의학 용어사전 대한 의사 협회
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine